What Epithelial Tissue Lines the Small and Large Intestines
Examples of body structures that have a lumen include the large intestine small intestine veins and arteries. Most of these cells also have short apical microvilli.

Locations And Functions Of Intestinal Epithelial Cells In The Small Download Scientific Diagram
Simple cuboidal with goblet cells.

. With the exception of the mouth and esophagus the rest of digestive tract consisting of the stomach small and large intestine is covered by these kinds of thin epithelia. Simple columnar epithelium lining the small intestine lumen consists of bothenterocytes andgoblet cells. Simple columnar with goblet cells.
The free surface of the columnar epithelium lining the small intestine is covered with microvilli. Remember that epithelia line or cover surfaces. Twothree layers of smooth muscle.
Composed of simple columnar epithelial cells it serves two main functions. Goblet cells are an example of a unicellular gland type found extensively in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine. Which of the following types of epithelial tissue lines the small and large intestine.
The multicellular exocrine glands known as serous glands develop from simple epithelium to form a secretory surface that secretes directly into an inner cavity. Dysfunction of IECs can cause diseases. The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface of both the small and large intestine of the gastrointestinal tract.
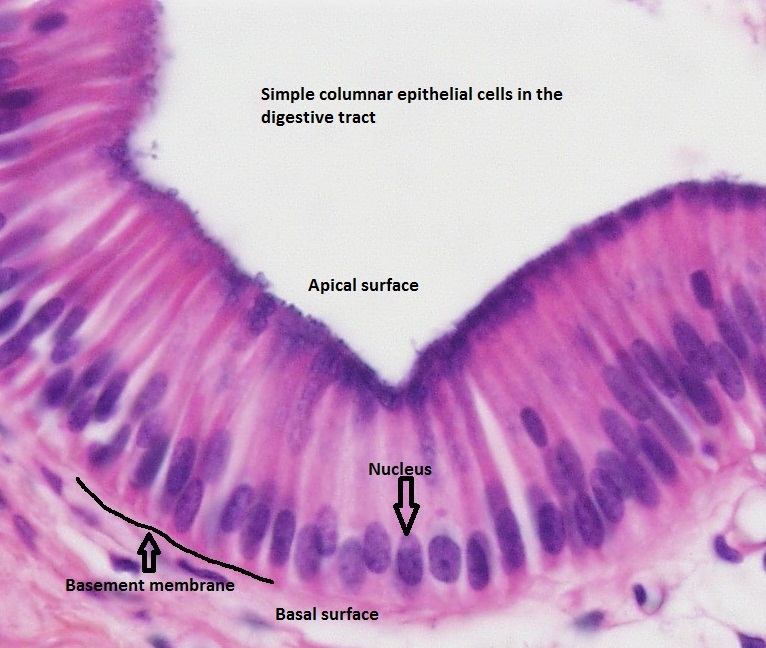
A tissue that lines both interior and exterior surfaces eg. Absorbing useful substances into the body and restricting the entry of harmful substances. They rest on a thinbasement membrane which separates them from thelamina propria.
Stomachsmall and large intestines and gall bladder. A simple columnar epithelium is a columnar epithelium that is uni-layered. Crypts of Leiberkuhn - longer less coiled.
Multicellular exocrine glands are composed of two or more cells which either secrete their contents directly into an inner body cavity eg serous glands or release their contents into a duct. Simple cuboidal epithelium-Lines small excretory ducts in various organs. What type of epithelium lines the small intestine.
The inner surface of stomach is lined by Gastric epithelium and that of the small intestine is lined by Intestinal epithelium. It is only one cell layer thick and columnar as the cells are rather tall. Flask-shaped goblet cells however have.
Simple columnar with goblet cells. You can see that this type of epithelium which is lining the lumen of the jejunum of the small intestine is a simple epithelium. Simple columnar with goblet cells and cola.
Both the gastric epithelium and intestinal epithelium are simple. Simple columnar epithelia line the uterus. Non-ciliated cells are seen in the stomach small intestine large intestine and rectumThese cells are often seen with a brush border where the apical surface of their plasma membrane is covered in minute actin-based projections called.
The unicellular glands are scattered single cells such as goblet cells found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine. The multicellular exocrine glands known as serous glands develop from simple epithelium to form a secretory surface. As part of its protective role the intestinal epithelium forms an important.
Circle one twothree pairs of salivary glands. Microvilli provide a very large surface area for the absorption of nutrients from the small intestine. These epithelia are usually thin containing cilia or microvilli and are often made of one layer of cells.
EPITHELIAL TISSUE HISTOLOGY EASY REVISION. Ciliated cells of these epithelia are found in the fallopian tubes and endometrium and are involved in the movement of the ovum. Posted by docaesthetic August 14.
Their free surfaces show a prominent distinctlystriated border. In slide 29 and slide 176 this type of epithelium lines the luminal mucosal surface of the small and large intestines respectively. Anteriorposterior to the trachea.
Which of the following types of epithelial tissue lines the small and large Intestine. What kind of epithelial tissue lines the small and large intestines. Skin the lining of the stomach and intestines the lining of the urinary tract etc.
Goblet cells - more than small intestine. The development maintenance and functions of IECs are strongly influenced by external nutrition. Intestinal epithelial cells IECs line the surface of intestinal epithelium where they play important roles in the digestion of food absorption of nutrients and protection of the human body from microbial infections and others.
Enterocytes about 25 µm high and 8-10 µm wide have a basal oval nucleus. Simple columnar with goblet cells and microvilli. Refer to the diagram at the end of this chapter for the tissue orientation and consult the atlas for the cell types that make up the epithelium.
The unicellular glands are scattered single cells such as goblet cells found in the mucous membranes of the small and large intestine. The lumen is the opening inside a tubular body structure that is lined by body tissue known as an epithelial membrane. In humans a simple columnar epithelium lines most organs of the digestive tract including the stomach small intestine and large intestine.
Simple columnar with goblet cells and cilia. Simple cuboidal with goblet cells and cilia. In some places you can see the apical area where junctions are located.
Note the basal lamina at the base of the epithelium. Columnar epithelium forms the lining of the stomach and intestines. The lining of the stomach is formed from simple columnar epithelium without surface structures.
The intestinal epithelium which covers the small and large intestine is simple columnar and nonciliated. These cells secrete enzymes and play an important role in selectively absorbing digested food.

Large Intestine Histology Colon Labels Histology Slide Histology Slides Tissue Biology Anatomy And Physiology

Histology Slides Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical School Motivation
No comments for "What Epithelial Tissue Lines the Small and Large Intestines"
Post a Comment